Configure AWS PrivateLink for Postgres
The PrivateLink feature is available on the following dbt Cloud Enterprise tiers:
- Business Critical
- Virtual Private
To learn more about these tiers, contact us at sales@getdbt.com.
A Postgres database, hosted either in AWS or in a properly connected on-prem data center, can be accessed through a private network connection using AWS Interface-type PrivateLink. The type of Target Group connected to the Network Load Balancer (NLB) may vary based on the location and type of Postgres instance being connected, as explained in the following steps.
PrivateLink endpoints can't connect across cloud providers. For a PrivateLink connection to work, both dbt Cloud and the server (like Postgres) must be hosted on the same cloud provider. For example, AWS PrivateLink can’t connect to resources hosted on Azure, and Azure PrivateLink can’t connect to resources hosted on AWS.
Configuring Postgres interface-type PrivateLink
1. Provision AWS resources
Creating an Interface VPC PrivateLink connection requires creating multiple AWS resources in the account containing, or connected to, the Postgres instance:
-
Security Group (AWS hosted only) — If you are connecting to an existing Postgres instance, this likely already exists, however, you may need to add or modify Security Group rules to accept traffic from the Network Load Balancer (NLB) created for this Endpoint Service.
-
Target Group — The Target Group will be attached to the NLB to tell it where to route requests. There are various target types available for NLB Target Groups, so choose the one appropriate for your Postgres setup.
-
Target Type:
-
Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL - IP
-
Find the IP address of your RDS instance using a command line tool such as
nslookup <endpoint>ordig +short <endpoint>with your RDS DNS endpoint -
Note: With RDS Multi-AZ failover capabilities the IP address of your RDS instance can change, at which point your Target Group would need to be updated. See this AWS blog post for more details and a possible solution.
-
-
On-prem Postgres server - IP
- Use the IP address of the on-prem Postgres server linked to AWS through AWS Direct Connect or a Site-to-Site VPN connection
-
Postgres on EC2 - Instance/ASG (or IP)
-
If your Postgres instance is hosted on EC2 the instance Target Group type (or ideally using the instance type to connect to an auto-scaling group) can be used to attach the instance without needing a static IP address
-
The IP type can also be used, with the understanding that the IP of the EC2 instance can change if the instance is relaunched for any reason
-
-
-
Target Group protocol: TCP
-
-
Network Load Balancer (NLB) — Requires creating a Listener that attaches to the newly created Target Group for port
5432- Scheme: Internal
- IP address type: IPv4
- Network mapping: Choose the VPC that the VPC Endpoint Service and NLB are being deployed in, and choose subnets from at least two Availability Zones.
- Security Groups: The Network Load Balancer (NLB) associated with the VPC endpoint service must either not have an associated security group, or the security group must have a rule that allows requests from the appropriate dbt Cloud private CIDR(s). Note that this is different than the static public IPs listed on the dbt Cloud Access, Regions, & IP addresses page. dbt Support can provide the correct private CIDR(s) upon request. If necessary, until you can refine the rule to the smaller CIDR provided by dbt, allow connectivity by temporarily adding an allow rule of
10.0.0.0/8. - Listeners: Create one listener per target group that maps the appropriate incoming port to the corresponding target group (details).
-
VPC Endpoint Service — Attach to the newly created NLB.
- Acceptance required (optional) — Requires you to accept our connection request after dbt creates the endpoint.
We highly recommend cross-zone load balancing for your NLB or Target Group; some connections may require it. Cross-zone load balancing may also improve routing distribution and connection resiliency. Note that cross-zone connectivity may incur additional data transfer charges, though this should be minimal for requests from dbt Cloud.
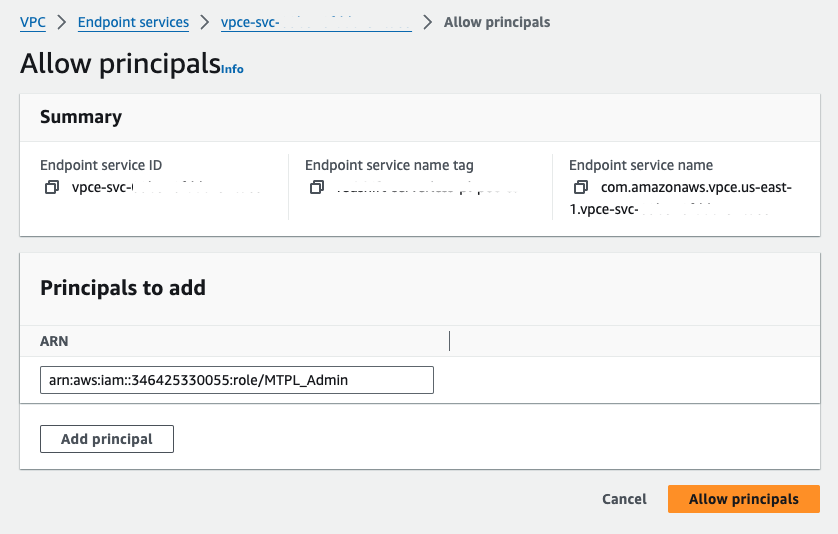
2. Grant dbt AWS account access to the VPC Endpoint Service
On the provisioned VPC endpoint service, click the Allow principals tab. Click Allow principals to grant access. Enter the ARN of the root user in the appropriate production AWS account and save your changes.
- Principal:
arn:aws:iam::346425330055:role/MTPL_Admin
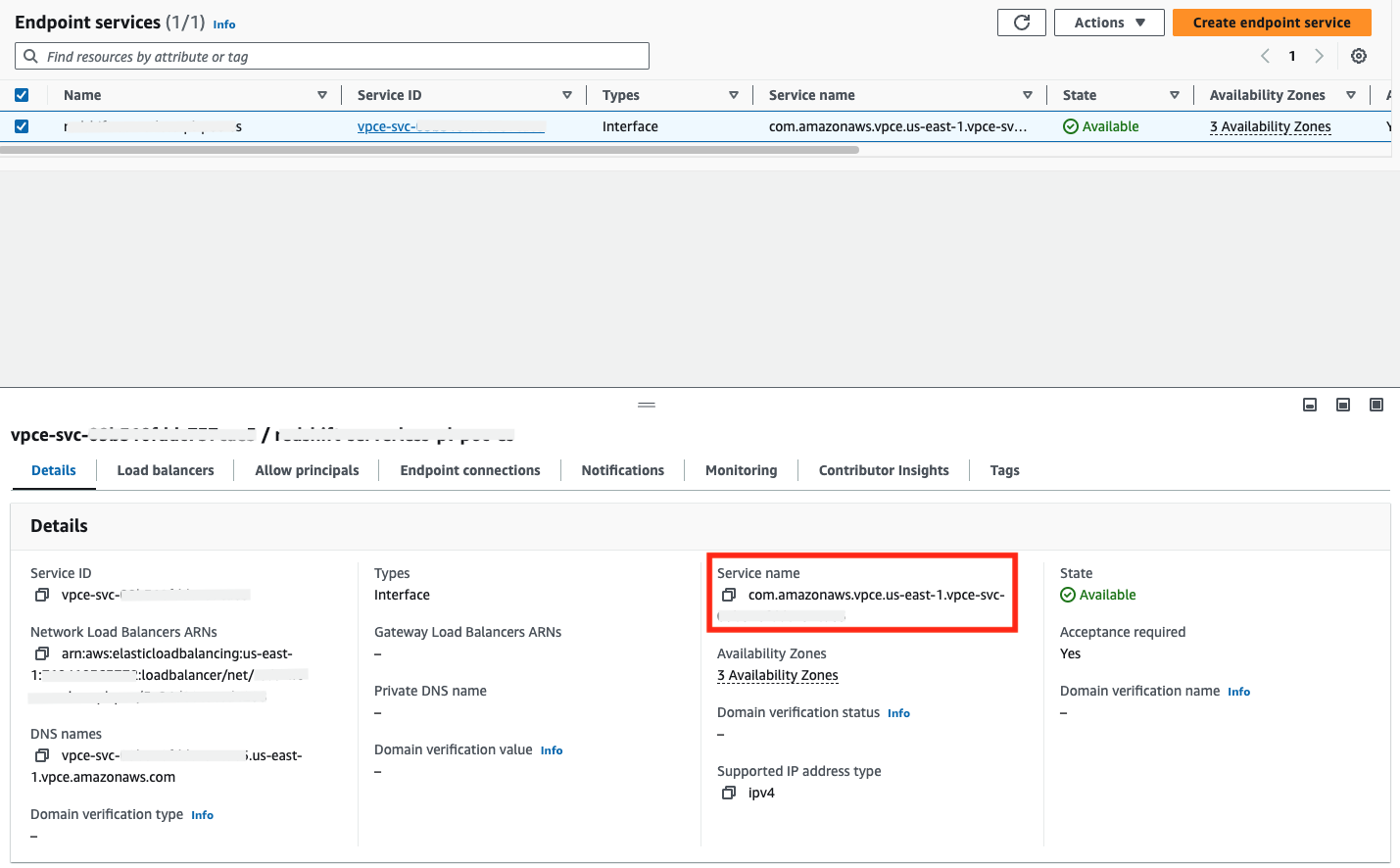
3. Obtain VPC Endpoint Service Name
Once the VPC Endpoint Service is provisioned, you can find the service name in the AWS console by navigating to VPC → Endpoint Services and selecting the appropriate endpoint service. You can copy the service name field value and include it in your communication to dbt Cloud support.
4. Add the required information to the template below, and submit your request to dbt Support:
Subject: New Multi-Tenant PrivateLink Request
- Type: Postgres Interface-type
- VPC Endpoint Service Name:
- Postgres server AWS Region (e.g., us-east-1, eu-west-2):
- dbt Cloud multi-tenant environment (US, EMEA, AU):
dbt Labs will work on your behalf to complete the PrivateLink setup. Please allow 3-5 business days for this process to complete. Support will contact you when the endpoint is available.
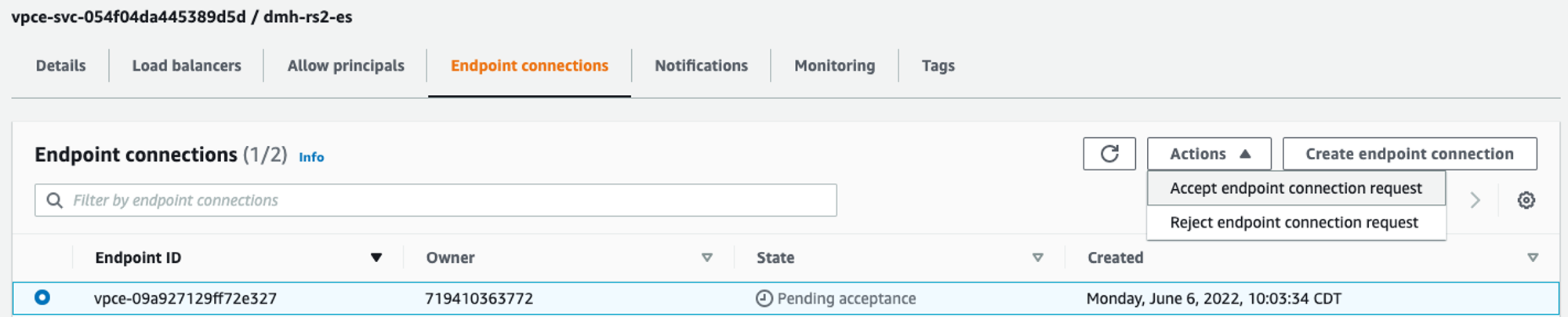
5. Accepting the connection request
When you have been notified that the resources are provisioned within the dbt Cloud environment, you must accept the endpoint connection (unless the VPC Endpoint Service is set to auto-accept connection requests). Requests can be accepted through the AWS console, as seen below, or through the AWS CLI.
Create Connection in dbt Cloud
Once dbt Cloud support completes the configuration, you can start creating new connections using PrivateLink.
- Navigate to settings → Create new project → select PostgreSQL
- You will see two radio buttons: Public and Private. Select Private.
- Select the private endpoint from the dropdown (this will automatically populate the hostname/account field).
- Configure the remaining data platform details.
- Test your connection and save it.
Troubleshooting
If the PrivateLink endpoint has been provisioned and configured in dbt Cloud, but connectivity is still failing, check the following in your networking setup to ensure requests and responses can be successfully routed between dbt Cloud and the backing service.
Configuration
Start with the configuration:
Monitoring
To help isolate connection issues over a PrivateLink connection from dbt Cloud, there are a few monitoring sources that can be used to verify request activity. Requests must first be sent to the endpoint to see anything in the monitoring. Contact dbt Support to understand when connection testing occurred or request new connection attempts. Use these times to correlate with activity in the following monitoring sources.